Solar energy is rapidly becoming one of the most sought-after sources of renewable energy worldwide. Whether you’re a homeowner looking to save on utility bills or someone curious about sustainable living, understanding the basics of solar power is essential. This guide breaks down the key aspects of solar energy, how it works, and why it’s worth considering.
What Is Solar Energy?
Solar energy is the power harnessed from the sun’s rays. Through technological advancements, this abundant energy source can be converted into electricity or heat for various uses. Solar power is renewable, environmentally friendly, and widely available, making it a cornerstone in the global shift towards cleaner energy.
How Does Solar Power Work?
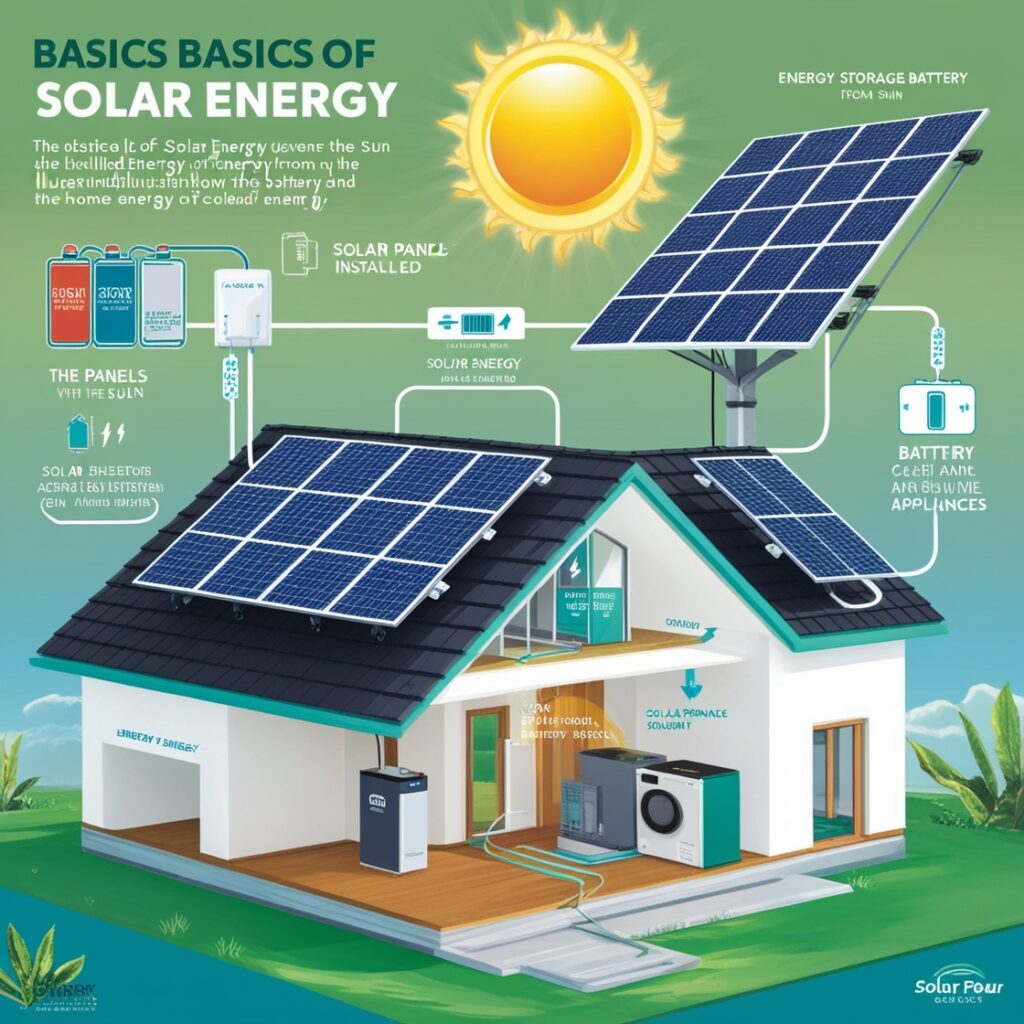
Solar energy is captured and converted using solar panels, also known as photovoltaic (PV) panels. Here’s a simplified breakdown of the process:
- Sunlight Absorption: Solar panels, composed of multiple solar cells, absorb sunlight.
- Electricity Generation: Photovoltaic cells convert the sunlight into direct current (DC) electricity.
- Conversion to Usable Power: An inverter converts DC electricity into alternating current (AC), which powers homes and businesses.
- Usage and Storage: The generated electricity can either be used immediately, stored in batteries, or fed back into the grid.
Benefits of Solar Energy
Switching to solar energy comes with numerous advantages:
- Reduced Energy Bills: By generating your electricity, you lower dependence on grid power and save money.
- Environmental Impact: Solar power significantly reduces greenhouse gas emissions compared to fossil fuels.
- Energy Independence: With solar panels, you’re less affected by power outages or rising energy costs.
- Long-Term Investment: Solar installations add value to properties and typically pay for themselves over time.
Types of Solar Power Systems
There are three primary types of solar power systems, each suited for different needs:
- Grid-Tied Systems:
- Connected to the local electricity grid.
- Excess power can be sold back to the grid.
- Ideal for areas with reliable grid access.
- Off-Grid Systems:
- Operate independently of the grid.
- Require battery storage for nighttime and cloudy days.
- Suitable for remote locations.
- Hybrid Systems:
- Combine grid access and battery storage.
- Provide greater flexibility and reliability.

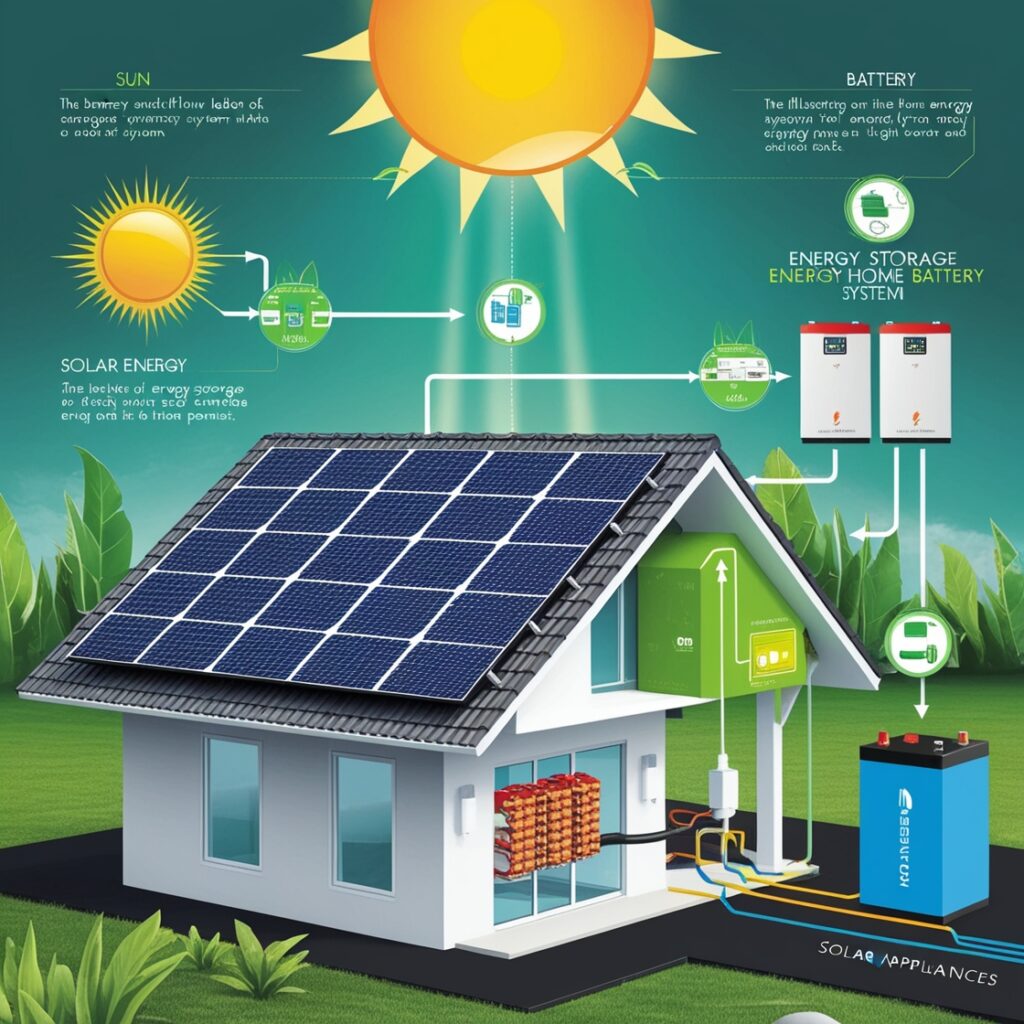
Key Components of a Solar Power System
A functioning solar power system typically includes:
- Solar Panels: Capture sunlight and convert it into electricity.
- Inverter: Transforms DC electricity into AC electricity.
- Mounting System: Secures the panels in place, either on rooftops or the ground.
- Battery Storage (optional): Stores excess electricity for later use.
- Charge Controller (for off-grid systems): Regulates battery charging and prevents overcharging.
Factors to Consider Before Installing Solar Panels
If you’re considering solar installation, keep these factors in mind:
- Location and Sunlight Availability:
- Regions with high solar exposure yield better energy output.
- Shading from trees or buildings can reduce efficiency.
- Roof Condition:
- Ensure your roof is structurally sound and can support the panels.
- South-facing roofs in the Northern Hemisphere typically perform best.
- System Size and Energy Needs:
- Calculate your household’s energy consumption.
- Choose a system size that meets your needs and fits your budget.
- Budget and Incentives:
- Solar installations can be costly upfront but are eligible for various tax credits and rebates.
- Research local incentives to offset initial costs.
- Maintenance Requirements:
- Solar systems are generally low-maintenance but require occasional cleaning and inspections.
Challenges of Solar Energy
While solar power is advantageous, it’s not without challenges:
- Initial Costs: The upfront cost of panels and installation can be high.
- Weather Dependence: Solar panels are less effective during cloudy days and at night.
- Energy Storage: Batteries for storing solar energy can be expensive.
- Space Requirements: Sufficient space is needed for panels to capture enough sunlight.
Future of Solar Energy
The future of solar energy is bright, with advancements in technology driving down costs and increasing efficiency. Emerging innovations include:
- Bifacial Solar Panels: Capture sunlight from both sides for greater efficiency.
- Solar Roof Tiles: Integrate seamlessly with traditional roofing.
- Improved Battery Technologies: Offer higher storage capacities and longer lifespans.
- Floating Solar Farms: Utilize water bodies to expand solar capacity.
Conclusion
Solar energy represents a sustainable and practical solution for reducing carbon footprints and achieving energy independence. By understanding the basics of solar power, you can make informed decisions about incorporating this renewable energy into your life. Whether you’re installing a small residential system or considering large-scale solar investments, the benefits of solar power are undeniable. Start your journey towards a greener future today—the sun’s energy is yours to harness.










1 thought on “Understanding Solar Power: A Comprehensive Guide to the Basics”
Comments are closed.